How to resolve Hash Collision?
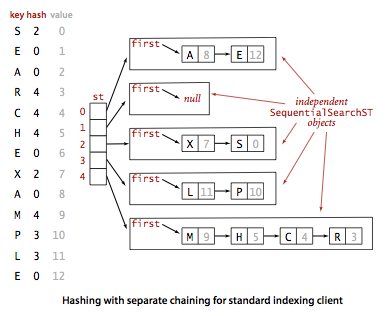
Hashing with separate chaining.
A hash function converts keys into array indices. The second component of a hashing algorithm is collision resolution: a strategy for handling the case when two or more keys to be inserted hash to the same index. A straightforward approach to collision resolution is to build, for each of the M array indices, a linked list of the key-value pairs whose keys hash to that index. The basic idea is to choose M to be sufficiently large that the lists are sufficiently short to enable efficient search through a two-step process: hash to find the list that could contain the key, then sequentially search through that list for the key.
Code (Java):/*************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac SeparateChainingHashST.java
* Execution: java SeparateChainingHashST
*
* A symbol table implemented with a separate-chaining hash table.
*
* % java SeparateChainingHashST
*
*************************************************************************/
public class SeparateChainingHashST<Key, Value> {
private static final int INIT_CAPACITY = 4;
// largest prime <= 2^i for i = 3 to 31
// not currently used for doubling and shrinking
// private static final int[] PRIMES = {
// 7, 13, 31, 61, 127, 251, 509, 1021, 2039, 4093, 8191, 16381,
// 32749, 65521, 131071, 262139, 524287, 1048573, 2097143, 4194301,
// 8388593, 16777213, 33554393, 67108859, 134217689, 268435399,
// 536870909, 1073741789, 2147483647
// };
private int N; // number of key-value pairs
private int M; // hash table size
private SequentialSearchST<Key, Value>[] st; // array of linked-list symbol tables
// create separate chaining hash table
public SeparateChainingHashST() {
this(INIT_CAPACITY);
}
// create separate chaining hash table with M lists
public SeparateChainingHashST(int M) {
this.M = M;
st = (SequentialSearchST<Key, Value>[]) new SequentialSearchST[M];
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
st[i] = new SequentialSearchST<Key, Value>();
}
// resize the hash table to have the given number of chains b rehashing all of the keys
private void resize(int chains) {
SeparateChainingHashST<Key, Value> temp = new SeparateChainingHashST<Key, Value>(chains);
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
for (Key key : st[i].keys()) {
temp.put(key, st[i].get(key));
}
}
this.M = temp.M;
this.N = temp.N;
this.st = temp.st;
}
// hash value between 0 and M-1
private int hash(Key key) {
return (key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % M;
}
// return number of key-value pairs in symbol table
public int size() {
return N;
}
// is the symbol table empty?
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
// is the key in the symbol table?
public boolean contains(Key key) {
return get(key) != null;
}
// return value associated with key, null if no such key
public Value get(Key key) {
int i = hash(key);
return st[i].get(key);
}
// insert key-value pair into the table
public void put(Key key, Value val) {
if (val == null) {
delete(key);
return;
}
// double table size if average length of list >= 10
if (N >= 10*M) resize(2*M);
int i = hash(key);
if (!st[i].contains(key)) N++;
st[i].put(key, val);
}
// delete key (and associated value) if key is in the table
public void delete(Key key) {
int i = hash(key);
if (st[i].contains(key)) N--;
st[i].delete(key);
// halve table size if average length of list <= 2
if (M > INIT_CAPACITY && N <= 2*M) resize(M/2);
}
// return keys in symbol table as an Iterable
public Iterable<Key> keys() {
Queue<Key> queue = new Queue<Key>();
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
for (Key key : st[i].keys())
queue.enqueue(key);
}
return queue;
}
/***********************************************************************
* Unit test client.
***********************************************************************/
public static void main(String[] args) {
SeparateChainingHashST<String, Integer> st = new SeparateChainingHashST<String, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; !StdIn.isEmpty(); i++) {
String key = StdIn.readString();
st.put(key, i);
}
// print keys
for (String s : st.keys())
StdOut.println(s + " " + st.get(s));
}
}
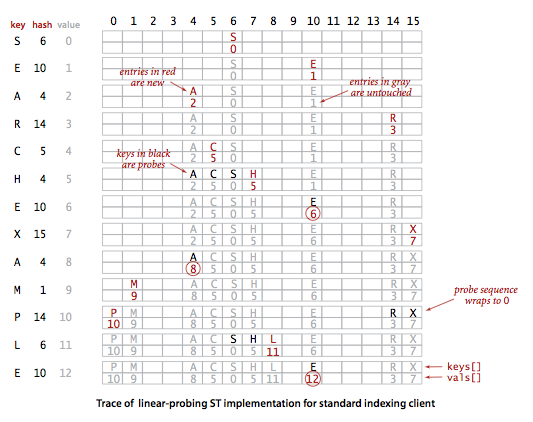
Hashing with linear probing.
Another approach to implementing hashing is to store N key-value pairs in a hash table of size M > N, relying on empty entries in the table to help with with collision resolution. Such methods are called open-addressing hashing methods. The simplest open-addressing method is called linear probing: when there is a collision (when we hash to a table index that is already occupied with a key different from the search key), then we just check the next entry in the table (by incrementing the index). There are three possible outcomes:- key equal to search key: search hit
- empty position (null key at indexed position): search miss
- key not equal to search key: try next entry
/*************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac LinearProbingHashST.java
* Execution: java LinearProbingHashST
*
* Symbol table implementation with linear probing hash table.
*
* % java LinearProbingHashST
* 128.112.136.11
* 208.216.181.15
* null
*
*
*************************************************************************/
public class LinearProbingHashST<Key, Value> {
private static final int INIT_CAPACITY = 4;
private int N; // number of key-value pairs in the symbol table
private int M; // size of linear probing table
private Key[] keys; // the keys
private Value[] vals; // the values
// create an empty hash table - use 16 as default size
public LinearProbingHashST() {
this(INIT_CAPACITY);
}
// create linear proving hash table of given capacity
public LinearProbingHashST(int capacity) {
M = capacity;
keys = (Key[]) new Object[M];
vals = (Value[]) new Object[M];
}
// return the number of key-value pairs in the symbol table
public int size() {
return N;
}
// is the symbol table empty?
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
// does a key-value pair with the given key exist in the symbol table?
public boolean contains(Key key) {
return get(key) != null;
}
// hash function for keys - returns value between 0 and M-1
private int hash(Key key) {
return (key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % M;
}
// resize the hash table to the given capacity by re-hashing all of the keys
private void resize(int capacity) {
LinearProbingHashST<Key, Value> temp =
new LinearProbingHashST<Key, Value>(capacity);
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
if (keys[i] != null) {
temp.put(keys[i], vals[i]);
}
}
keys = temp.keys;
vals = temp.vals;
M = temp.M;
}
// insert the key-value pair into the symbol table
public void put(Key key, Value val) {
if (val == null) {
delete(key);
return;
}
// double table size if 50% full
if (N >= M/2) resize(2*M);
int i;
for (i = hash(key); keys[i] != null; i = (i + 1) % M) {
if (keys[i].equals(key)) { vals[i] = val; return; }
}
keys[i] = key;
vals[i] = val;
N++;
}
// return the value associated with the given key, null if no such value
public Value get(Key key) {
for (int i = hash(key); keys[i] != null; i = (i + 1) % M)
if (keys[i].equals(key))
return vals[i];
return null;
}
// delete the key (and associated value) from the symbol table
public void delete(Key key) {
if (!contains(key)) return;
// find position i of key
int i = hash(key);
while (!key.equals(keys[i])) {
i = (i + 1) % M;
}
// delete key and associated value
keys[i] = null;
vals[i] = null;
// rehash all keys in same cluster
i = (i + 1) % M;
while (keys[i] != null) {
// delete keys[i] an vals[i] and reinsert
Key keyToRehash = keys[i];
Value valToRehash = vals[i];
keys[i] = null;
vals[i] = null;
N--;
put(keyToRehash, valToRehash);
i = (i + 1) % M;
}
N--;
// halves size of array if it's 12.5% full or less
if (N > 0 && N <= M/8) resize(M/2);
assert check();
}
// return all of the keys as in Iterable
public Iterable<Key> keys() {
Queue<Key> queue = new Queue<Key>();
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
if (keys[i] != null) queue.enqueue(keys[i]);
return queue;
}
// integrity check - don't check after each put() because
// integrity not maintained during a delete()
private boolean check() {
// check that hash table is at most 50% full
if (M < 2*N) {
System.err.println("Hash table size M = " + M + "; array size N = " + N);
return false;
}
// check that each key in table can be found by get()
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
if (keys[i] == null) continue;
else if (get(keys[i]) != vals[i]) {
System.err.println("get[" + keys[i] + "] = "
+ get(keys[i]) + "; vals[i] = " + vals[i]);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/***********************************************************************
* Unit test client.
***********************************************************************/
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinearProbingHashST<String, Integer> st = new LinearProbingHashST<String, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; !StdIn.isEmpty(); i++) {
String key = StdIn.readString();
st.put(key, i);
}
// print keys
for (String s : st.keys())
StdOut.println(s + " " + st.get(s));
}
}
No comments:
Post a Comment