Consider all the leaves of a binary tree. From left to right order, the values of those leaves form a leaf value sequence.
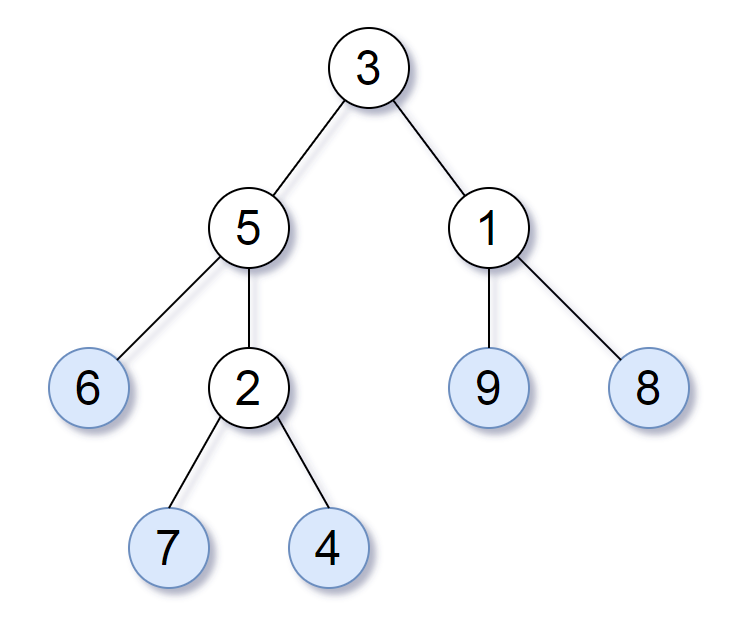
For example, in the given tree above, the leaf value sequence is
(6, 7, 4, 9, 8).
Two binary trees are considered leaf-similar if their leaf value sequence is the same.
Return
true if and only if the two given trees with head nodes root1 and root2 are leaf-similar.
Note:
- Both of the given trees will have between
1and100nodes.
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean leafSimilar(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if (root1 == null) {
return root2 == null;
}
if (root2 == null) {
return root1 == null;
}
List<Integer> sequence1 = findLeafValueSequence(root1);
List<Integer> sequence2 = findLeafValueSequence(root2);
if (sequence1.size() != sequence2.size()) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < sequence1.size(); i++) {
int num1 = sequence1.get(i);
int num2 = sequence2.get(i);
if (num1 != num2) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private List<Integer> findLeafValueSequence(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
findLeafValueSequenceHelper(root, ans);
return ans;
}
private void findLeafValueSequenceHelper(TreeNode root, List<Integer> ans) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
ans.add(root.val);
return;
}
findLeafValueSequenceHelper(root.left, ans);
findLeafValueSequenceHelper(root.right, ans);
}
}
No comments:
Post a Comment